Deciding between a Simple IRA and 401k plan for your small business can be confusing. Both plans have advantages and disadvantages in terms of costs, contribution limits, employer requirements and more. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll compare Simple IRAs and 401ks to help you determine which option may lead to the most profit for your business.
What is a Simple IRA?
A Simple IRA, or Savings Incentive Match Plan for Employees, is a retirement plan designed specifically for small businesses with 100 or fewer employees. The Simple IRA gives small business owners a simplified way to contribute toward their employee’s retirement and reap tax benefits.
Some key features of Simple IRAs:
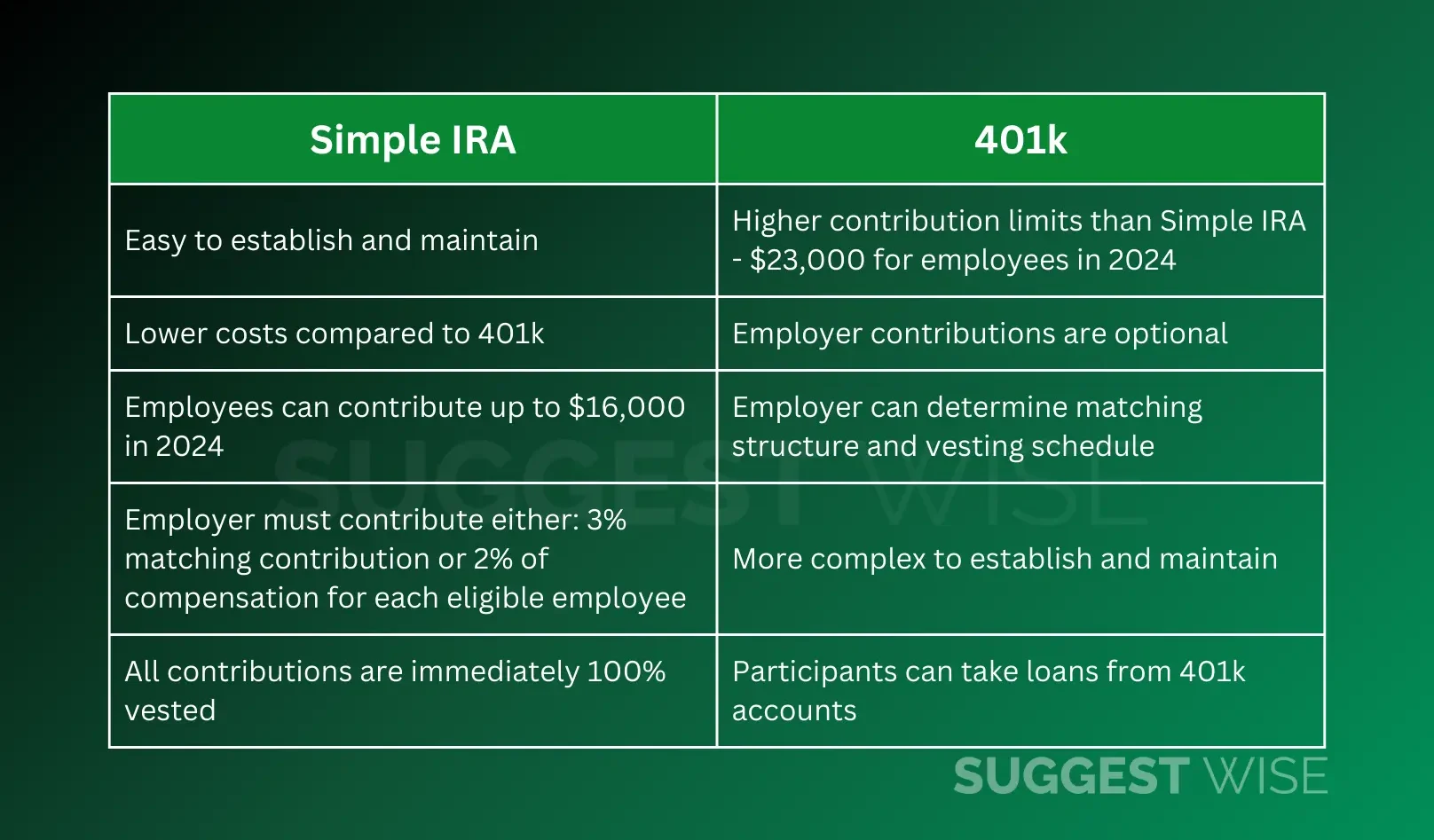
- Easy to establish and maintain
- Lower costs compared to 401k
- Employees can contribute up to $16,000 in 2024
- Employer must contribute either:
- 3% matching contribution
- 2% of compensation for each eligible employee
- All contributions are immediately 100% vested
Simple IRAs provide a straightforward, low-cost retirement savings option for small business owners. The required employer contributions also make it easy for businesses to offer a retirement plan without deciding on match amounts and vesting schedules.
What is a 401k Plan?
A 401k is likely the most well-known employer-sponsored retirement account. 401k plans are available to businesses of any size.
Some key 401k features:
- Higher contribution limits than Simple IRA – $23,000 for employees in 2024
- Employer contributions are optional
- Employer can determine matching structure and vesting schedule
- More complex to establish and maintain
- Participants can take loans from 401k accounts
401k plans offer larger tax-advantaged contribution room for employees. They also give employers more flexibility in designing matches and vesting. However, 401ks come with more administrative responsibilities and higher costs.
Also Read: IRA vs. 401(k): Key Differences and Benefits to Consider
Simple IRA vs 401k: Key Differences
Now that we’ve covered the basics of Simple IRAs and 401k plans, let’s compare them across some key factors:
Eligibility
Simple IRAs are for businesses with 100 or fewer employees. 401k plans have no size restrictions.
For Simple IRAs, employees must earn $5,000 in any 2 preceding years and expect $5,000 in the current year. 401k eligibility is typically 21+ years old and 1 year of service.
Contribution Limits
In 2024, employee contribution limits are:
- Simple IRA: $16,000
- 401k: $23,000
Catch-up contributions for those 50+ are $3,500 for Simple IRA and $7,500 for 401k.
Employer Contributions
SIMPLE IRA employers must contribute:
- 3% match
- 2% of compensation for all
401k employer contributions are optional. Matches and vesting are flexible.
Administrative Considerations
Simple IRAs have minimal reporting requirements. 401ks require nondiscrimination testing, Form 5500 filings, and more.
Costs
Simple IRAs have very low costs. 401ks can have high recordkeeping, compliance, and investment fees.
Simple IRA vs 401k: Which is More Profitable?
So which retirement plan will lead to the most profit for your small business? Here are some key factors to consider:
Your Number of Employees
If you have 100 or fewer employees, a Simple IRA may be your only option. The costs of establishing and administering a 401k often outweigh the benefits for very small companies.
As you grow toward 100 employees, you may want to consider switching to a 401k for the higher contribution limits. But keep costs in mind.
Salary Levels
Average salary levels in your company should guide your choice.
For lower salaried staff, Simple IRA limits of $16,000 are often sufficient. Employees earning higher incomes will benefit more from the $23,000 401k limits.
Your Profit Margins
A 401k plan can cost between $1,500 – $6,000 per year. If your profits are narrow, keeping costs down with a Simple IRA may be key.
Companies with higher earnings can likely absorb 401k administrative fees more easily in exchange for higher contributions.
Your Matching Goals
401k plans give you flexibility in employer matches. You can match a percentage of employee contributions or base it on profitability each year.
With a Simple IRA, you must contribute either a 3% match or 2% of compensation. Consider which option best aligns with your financial goals.
Employee Retention Needs
The vesting schedules allowed with 401k plans can improve employee retention. Employees must remain employed for a set period to be fully vested in your contributions.
If you anticipate high turnover, the immediate 100% vesting of Simple IRAs may be preferred.
Choose the Right Plan for Your Small Business
As you can see, there are many factors to weigh when choosing between Simple IRA and 401k plans. Consider costs, employee eligibility, your profit margins and other key factors.
Most importantly, make sure you choose a plan that provides adequate tax-advantaged retirement savings opportunities for your valued employees. The plan that leads to the most profit is the one that best balances employee needs, business costs, and your own savings goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
Still deciding between Simple IRA vs 401k? Here are answers to some frequently asked questions:
Can I have both a Simple IRA and 401k plan?
No, an employer cannot sponsor both a Simple IRA and 401k. You must choose one or the other.
What happens if I outgrow the 100 employee Simple IRA limit?
You can continue operating your Simple IRA until the year after you exceed 100 employees. At that point, you’ll need to switch to a 401k or other qualified plan.
Can I make additional retirement contributions beyond the Simple IRA limits?
Yes, employees can make additional personal contributions to IRAs or Roth IRAs up to the annual limits. Their eligibility to deduct these contributions depends on their income.
Are there tax benefits to the employer for contributions?
Yes, both Simple IRA and 401k contributions can be claimed as tax deductible business expenses. This provides significant tax savings.
Can I offer matching and non-elective contributions?
No, with a Simple IRA you must choose between a full 3% match or 2% non-elective contribution. The non-elective option provides cost consistency.
